“An economic model based on sharing underutilized assets from spaces to skills to stuff for monetary or non-monetary benefits. Rachel Botsman”.
“A social and economic system driven by network technologies and peer communities that enables the sharing of underutilized assets from space to skills to objects and money, transforming how we produce, consume, finance and learn”.
Anything you can buy, you can rent – even rent a friend.
Though not dwelling on the underlying principles, suffice it to say, there is a shift from individual ownership to shared access driven by convenience and choices across the value chain.
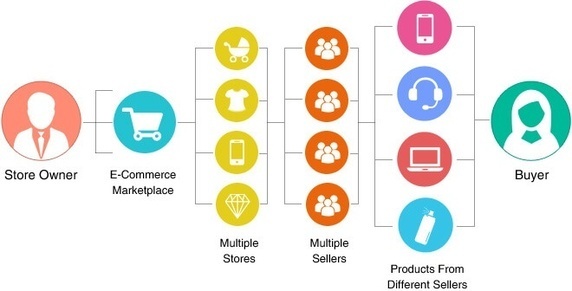
New business models, examples include eBay, Zipcar, Airbnb are wreaking havoc and causing disruptions across industries – retail, manufacturing, transport, food, office rentals to name a few.
Case in Point –
The rise of the sharing economy in India has been a revelation and seeing tremendous growth.
Key drivers affecting the growth of organized e-commerce rental market:
- Rising adoption of rentals due to lower prices and reduced expense and maintenance costs
- Increased smartphone penetration
- Independent lifestyle trend among young coupled with smaller places in urban areas
- Growth of peer to peer social networks &
- Desire for quality goods and services
Below are the major online rental companies in India.
- Furlenco (http://www.furlenco.com)
- Rentomojo (http://www.rentomojo.com)
- City Furnish (http://www.cityfurnish.com)
- Fabrento (http://www.fabrento.com)
- GrabOnRent (http://www.grabonrent.com)
- RentOnGo (http://www.rentongo.com)
- Guarented (http://www.guarented.com)
Business Model –
Viable, networked business models have evolved over traditional ownership along the lines of B2C, P2P and B2B.
- Rental
- On-demand
- Subscription
- Membership usage
- Try-and-buy
- Freemium (though not seen widely in India)
Factors Determining Growth –
Companies can embrace the sharing economy and stay profitable by connecting buyers and sellers over a virtual marketplace.
- Brand Penetration
- Highest Quality
- Features Vs Price Comparison
- Culture and Customer Experience
Furlenco.com – Amazing brand penetration, Pricy renting but with good terms
UrbanLadder – Trying to sell furniture on EMI
Convenience is the ultimate decider in this “Shared Economy”.
Points to Ponder –
- People can select and order goods & services across the spectrum through online monthly, quarterly, or annual rental packages.
- Business Model – Inhouse Vs Asset-light (typical example being Furlenco Vs Rentomojo).
- Revenues, Expenses, New Category of Products
- Expenses – Workforce requirement, distribution, design, contract labor, repair and maintenance, advertisements and promotions, depreciation and amortization costs
- Technology has enabled consumers to experience a new way of procuring goods and services giving rise to the question of Online Reputation.
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers, the sharing economy will generate potential revenues of $335 Bn by 2025 globally.
Considering that the benefits of the sharing economy model are visible, the potential for growth is great.
Will an asset-light model showing better numbers in the short-term work or an Inhouse model with great customer experience wins, is the ultimate question for the shared economy in India.
Thoughts…